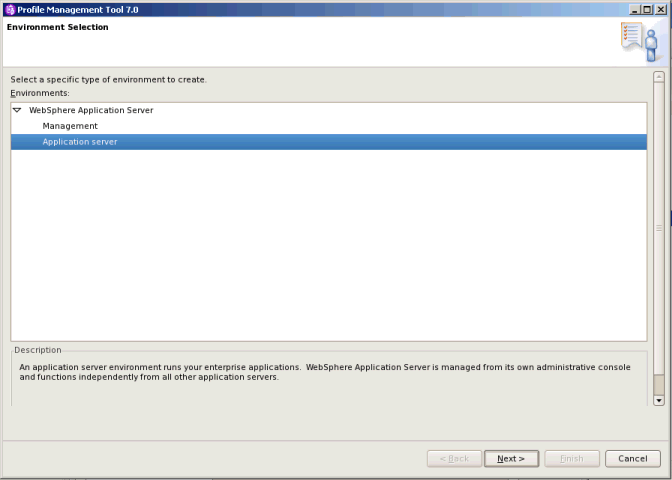
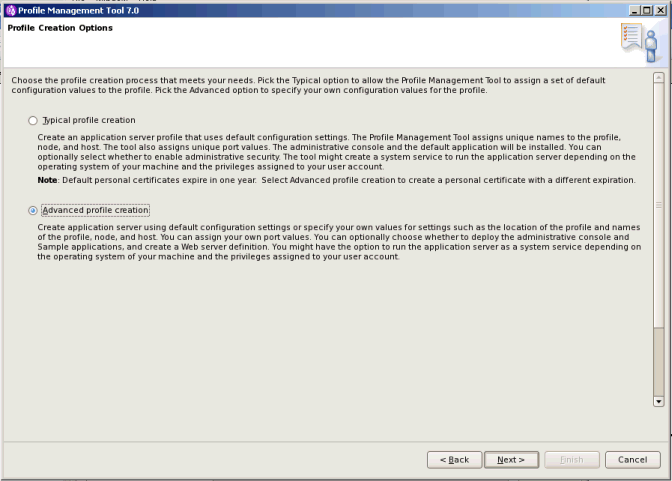
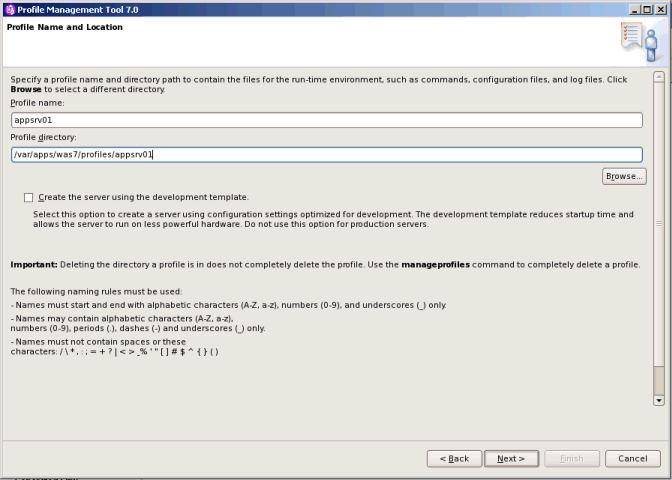
This article will be about console profile manager in WAS
Run manageprofiles -help or visit Information Center at: http://www14.software.ibm.com/webapp/wsbroker/redirect?version=pix&product=was-nd-dist&topic=rxml_manageprofiles
1. To list number of profiles, execute command
manageProfiles -listProfiles
eg.
C:\IBM\WebSphere\AppServer\bin>manageProfiles -listProfiles
2. To delete all the existing profiles, execute
C:\IBM\WebSphere\AppServer\bin>manageProfiles.bat -deleteAll
INSTCONFSUCCESS: Success: All profiles are deleted.
Once profile is deleted, remove left directories manually. To delete directories recursively in windows use command :
rmdir /s /q
3. Create new prfoiles including deployment manager Now this could be interesting which directory could be recommended, many user creates profiles under path WebSphere\AppServer\profiles\\, now this works without issue in unix flavor but in case if 32 bit Windows there is limitation of 255 characters in path. So many people prefer to create profiles like :\IBM\Profiles\\
Command to create new profile :
Syntax :
Command to create new profile :
Syntax :
manageProfiles -create -profileName -profilePath -templatePath -nodeName -cellName -hostname | -serverName -startingPort 10000 -winserviceCheck
eg : |
| C:\IBM\WebSphere\AppServer\bin>manageProfiles -create -profileName AppSrv01 -profilePath C:\IBM\profiles\AppSrv01 -nodeName AppSrv01Node -cellName AppSrv01Cell -hostname localhost -serverName server -startingPort 10000 -winserviceCheck false
gives output as |
INSTCONFSUCCESS: |
4. to check the ports assigned and other details for new profiles check the file at
\logs\AboutThisProfile.txt |
C:\IBM\WebSphere\AppServer\bin>type \IBM\profiles\AppSrv01\logs\AboutThisProfile.txt |
4. to check the ports assigned and other details for new profiles check the file at